题面
题面翻译
题目描述
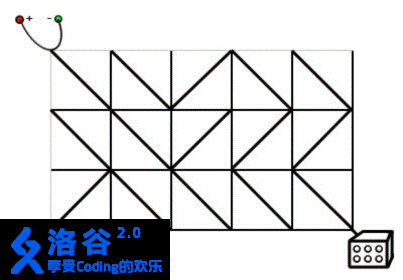
Casper 正在设计电路。有一种正方形的电路元件,在它的两组相对顶点中,有一组会用导线连接起来,另一组则不会。有 个这样的元件,你想将其排列成 行,每行 个。 电源连接到板的左上角。灯连接到板的右下角。只有在电源和灯之间有一条电线连接的情况下,灯才会亮着。为了打开灯,任何数量的电路元件都可以转动 90°(两个方向)。
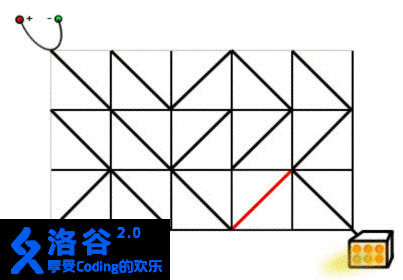
在上面的图片中,灯是关着的。如果右边的第二列的任何一个电路元件被旋转 90°,电源和灯都会连接,灯被打开。现在请你编写一个程序,求出最小需要多少旋转多少电路元件。
输入输出格式
输入格式
输入的第一行包含两个整数 和 ,表示盘子的尺寸。 在以下 行中,每一行有 个符号 \ 或 /,表示连接对应电路元件对角线的导线的方向。
输出格式:
如果可以打开灯,那么输出只包含一个整数,表示最少转动电路元件的数量。
如果不可能打开灯,输出 NO SOLUTION。
题目描述
Casper is designing an electronic circuit on a rectangular grid plate. There are square tiles that are aligned to the grid on the plate. Two (out of four) opposite corners of each tile are connected by a wire.
A power source is connected to the top left corner of the plate. A lamp is connected to the bottom right corner of the plate. The lamp is on only if there is a path of wires connecting power source to lamp. In order to switch the lamp on, any number of tiles can be turned by 90° (in both directions).
In the picture above the lamp is off. If any one of the tiles in the second column from the right is turned by 90° , power source and lamp get connected, and the lamp is on.
Write a program to find out the minimal number of tiles that have to be turned by 90° to switch the lamp on.
输入格式
The first line of input contains two integer numbers and , the dimensions of the plate. In each of the following lines there are symbols – either \ or / – which indicate the direction of the wire connecting the opposite vertices of the corresponding tile.
输出格式
There must be exactly one line of output. If it is possible to switch the lamp on, this line must contain only one integer number: the minimal number of tiles that have to be turned to switch on the lamp. If it is not possible, output the string: NO SOLUTION
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
3 5
\\/\\
\\///
/\\\\样例输出 #1
1提示
对于 的数据,,。
对于所有数据,。
思路
我们可以把它看成一个的一个点阵,然后对于\,那么它的左上角的点到右下角的点的边权就是,它的左下角到右上角边权就是,/也是同理。
所以我们可以建边然后跑最短路,但其实大可不必。
我们可以直接在这个二维矩阵上进行 01BFS ,分别判断四个方向。
什么时候没有答案呢?
对于对角线上的移动,横纵坐标之和是不变的,因此我们从出发,走到,假如不是偶数,那么就无解。
Tips:
C++中,\为转义字符,使用时记得写为\\。- 循环预处理比
memset要快。
当然,这种做法是超快的,一不小心就拿了个最优解:
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,m;
char e[550][550];
int dist[550][550];
int dx[]={-1,-1,1,1};//左上,右上,左下,右下
int dy[]={-1,1,-1,1};
inline int read()
{
int x=0,y=1;//x是什么,y是正负
char c=getchar();
while(c>'9'||c<'0')
{
if(c=='-') y=-1;
c=getchar();
}
while(c>='0'&&c<='9')
{
x=x*10+c-'0';
c=getchar();
}
return x*y;
}
struct point
{
int x,y,d;
point(){}
point(int a,int b,int c):x(a),y(b),d(c){}
};
//对于一个九宫格,以中间位置为参照,上下左右一定要和它不同,边权为0,否则为1.
//而四个角,则需要特殊处理,若为'\',则左上角和右下角必须和它相同,若为'/',则右上角和左下角必须相同
//应按照点
void _01BFS()
{
deque<point> q;
q.push_front(point(0,0,0));
dist[0][0]=0;
while(!q.empty())
{
point now=q.front();
q.pop_front();
if(now.x==n&&now.y==m) return;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
int nx=now.x+dx[i],ny=now.y+dy[i];
if(nx<0||ny<0||nx>n||ny>m) continue;
if(i==0)//左上
{
if(e[now.x][now.y]=='\\')
{
if(now.d<dist[nx][ny])
{
dist[nx][ny]=now.d;
q.push_front(point(nx,ny,dist[nx][ny]));
}
}
else//'/'
{
if(now.d+1<dist[nx][ny])
{
dist[nx][ny]=now.d+1;
q.push_back(point(nx,ny,dist[nx][ny]));
}
}
}
if(i==1)//右上
{
if(e[now.x][now.y+1]=='/')
{
if(now.d<dist[nx][ny])
{
dist[nx][ny]=now.d;
q.push_front(point(nx,ny,dist[nx][ny]));
}
}
else//'\'
{
if(now.d+1<dist[nx][ny])
{
dist[nx][ny]=now.d+1;
q.push_back(point(nx,ny,dist[nx][ny]));
}
}
}
if(i==2)//左下
{
if(e[now.x+1][now.y]=='/')
{
if(now.d<dist[nx][ny])
{
dist[nx][ny]=now.d;
q.push_front(point(nx,ny,dist[nx][ny]));
}
}
else//'\'
{
if(now.d+1<dist[nx][ny])
{
dist[nx][ny]=now.d+1;
q.push_back(point(nx,ny,dist[nx][ny]));
}
}
}
if(i==3)//右下
{
if(e[now.x+1][now.y+1]=='\\')
{
if(now.d<dist[nx][ny])
{
dist[nx][ny]=now.d;
q.push_front(point(nx,ny,dist[nx][ny]));
}
}
else//'/'
{
if(now.d+1<dist[nx][ny])
{
dist[nx][ny]=now.d+1;
q.push_back(point(nx,ny,dist[nx][ny]));
}
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
n=read(),m=read();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%s",e[i]+1);
if((n+m)%2!=0)
{
cout<<"NO SOLUTION"<<endl;
return 0;
}
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<=m;j++)
dist[i][j]=0x7fffffff;
_01BFS();
printf("%d",dist[n][m]);
return 0;
}